Impact of Twin Lockdowns on Hunger, Labor Market Outcomes, and Household Coping Mechanisms: Evidence from Uganda
With Shamma Adeeb Alam and Ishraq Ahmed
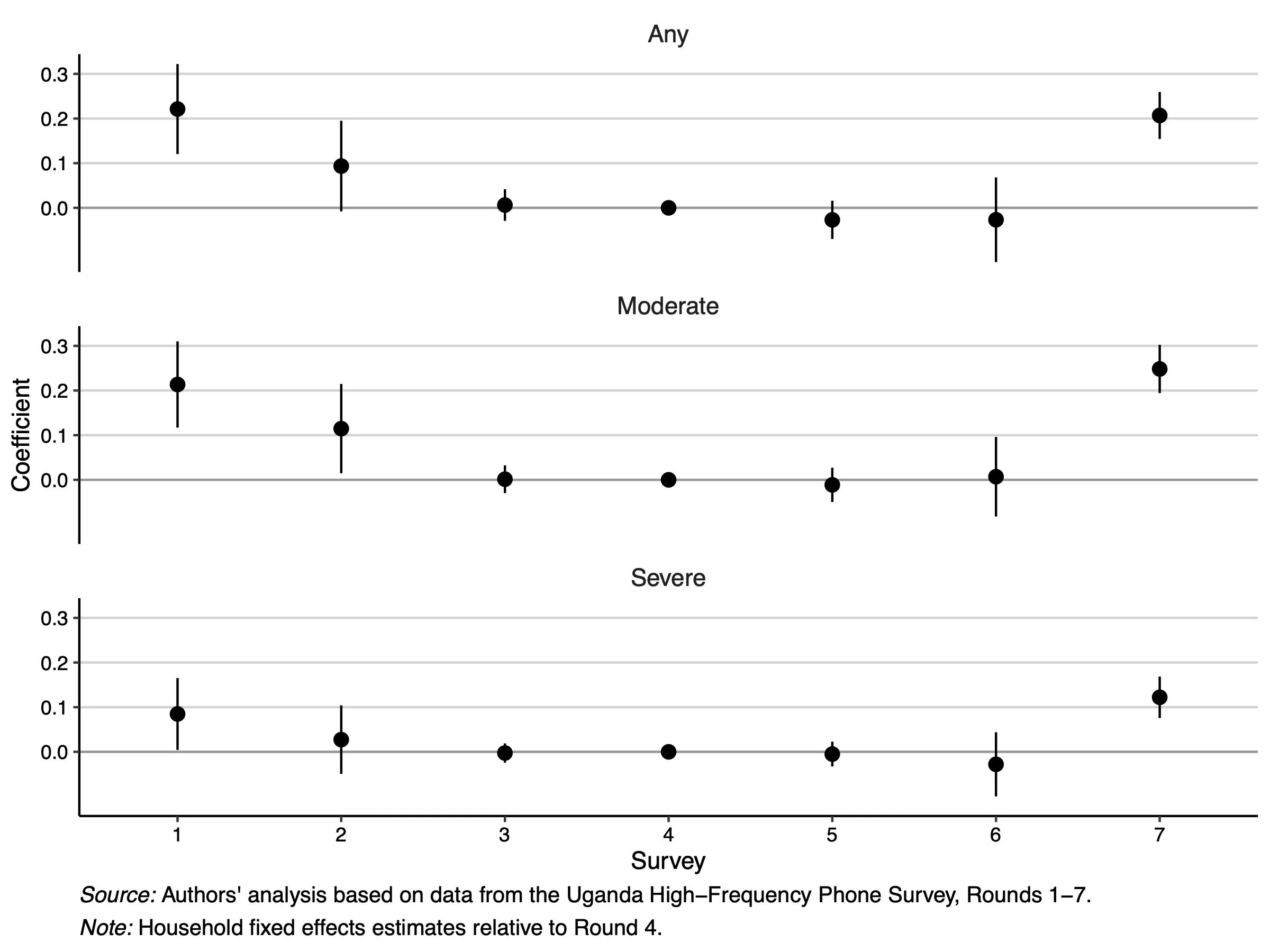
Above: The most severe lockdowns ended immediately before Round 1 and two months before Round 7.
Abstract:
Uganda had two of the strictest COVID-19 lockdowns in Sub-Saharan Africa. These severe lockdowns provide a unique case study for understanding the implications of such public-health measures on economic well-being. We use longitudinal data to examine the lockdowns’ short- and medium-term impacts on household food insecurity, labor-market outcomes, and coping strategies. Lockdowns significantly exacerbated food insecurity immediately and continued to do so in the medium term. The effect was more pronounced after the second lockdown, likely from a combination of reduced resilience after the first lockdown and lower-than-normal rainfall immediately before. There were substantial decreases in income from various sources—including agriculture, non-farm businesses, and wage employment—contributing to the heightened food insecurity. Notably, agricultural households were less adversely affected, and there was a significant switch to agricultural activities as a coping mechanism. The other coping mechanisms households typically rely on for idiosyncratic shocks, such as remittances and government assistance, failed, contributing to the sizeable increase in food insecurity.
GitHub repository with paper and code